Computerized Maintenance Management System Solution
One of the key strategy in the oil, gas and petrochemical industries, is maximizing value-added products and thus create long-term value for shareholders, paying particular attention to issues of productivity. With a closer look, it becomes clear that in order to achieve strategic objectives listed above, the following two main axes must be considered as general framework plans and operational plans:
- Asset Utilization
- Cost Structure Improvement
The most important key performance indicator of the readiness to Asset Utilization according to international standards and textbooks include:
- Availability
- Reliability
- Maintainability
- Safety
On the other hand the in production operating expenses (OPEX), cost of operation generally are fixed, but the cost of maintenance is very variable, depending on the quality of service and operation of maintenance management system.
Therefore, proper management and continuous follow-up activities in this field, gathering and processing of operational and financial data, to plan activities and measure progress toward goals and the effectiveness of them is of extreme importance. The most effective tool to apply the optimal management of maintenance, is CMMS.
SOLUTION
What is Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS)?
This software is used to determine and management the maintenance objectives, strategies and responsibilities, and implementation of them. By such tools, maintenance planning, maintenance activities control, and the improvement of maintenance activities and economics is realized.
What are the key benefits?
- Maintenance is recognized by management as an integrated, essential part of production
- The Maintenance management focus is upon making equipment available through increased reliability
- There is an emphasis on analysis of the reasons for down time and better work scheduling and repair things quicker
- There is a commitment to planned work and saving on budget and parts
- There is an emphasis on training
- Discover ways to improve and continuous improvement programs are in place
- Operators are involved in the maintenance of their equipment, preventative maintenance gets done and no lost work orders
Why Choose AIMS?
AIMS implements a CMMS by following requirements of dependability management standards, IEC60300 and asset management ISO 55000 and install a user-friendly Asset Integrity Management/CMMS software tools that called “CMMS³” in close partnership agreement with RAMCUBE Company. This software is embedded:
- MASTER TABLES
- Area codes /Disciplines /Functional Units /Item Types and Sub-Types /Failure Codes /Standard Operations /Human Resources /Tools/ spare part
- ENGINEERING
- Documents /Equipment /Models /Spare Parts /Tags /Tests (Measurement Points)
- MAINTENANCE
- Job Analysis /Maintenance Items /Maintenance Strategies (Plans) /Work Requests /Work Orders /Overhaul Maintenance /Budgeting /Planning/
- TYPE OF MAINTENANCE
- Preventive /Inspective /Corrective /Operational support /Improvement & Modifications
- KPI & REPORTING
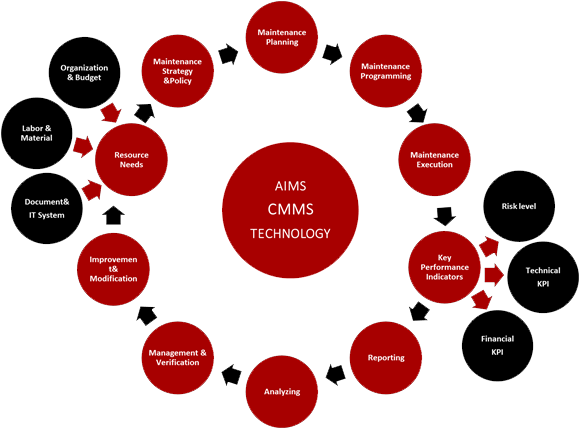
OUR APPROACH
Our experts have in-depth knowledge of the oil, gas, petrochemical, power, renewable energy, civil and infrastructure fields, in cooperation with our international partner implement and install of CMMS , in complete service outsourcing ,including :
- Strategy & policy
- Defining and establishing of maintenance strategy and policy that commit the organization to a realizable level of performance. The goals focus on ambition level for;
- risk, production and cost
- regulatory requirements
- Technical condition of the facility in particular the performance of safety systems and critical processes.
- Improvement of overall maintenance process.
- Maintenance planning &programming:
- Identifying failure modes, failure mechanisms and failure causes that can have a significant effect on safety and production shall bed and the
- Determining risk in order to establish a maintenance planning.
- Planning maintenance structure with a set of tasks that include the activities, procedures, resources and the time required to carry out maintenance. Planning consists of budgeting, long term planning, day to day planning and prioritizing.
- Programming maintenance activities includes maintenance interval and written procedures for maintaining, testing, and preparing the various components within the plant.
- Execution:
- Includes preparations, work permits, carrying out work and reporting mandatory information on the work order.
- Reporting:
- Involving collection and quality assurance of maintenance data, and presenting these to maintenance departments and management in the form of defined indicators particularly technical integrity data for safety functions.
- Analysis and Improvements:
- Involving carry out analysis of historical maintenance data, and unwanted incidents related to maintenance, e.g. trend analysis, root cause failure analysis.
- Resources (Organization, Materials & Documentation)
- Consisting of the people, their training, competence, job descriptions and work processes.
- Including consumables, spare parts and tools required to carry out maintenance.
- Optimizing spare part availability based on demand, consequence of failure, repair time and cost and linking to the maintenance planning activity.
- Including all documentation required to carry out and manage maintenance in an effective manner such as equipment/tag register, drawings and design details, historical maintenance data, maintenance task descriptions, spares lists,
- Management and verification
- Well organizing management team taking responsibilities in implementing the principles herein and verifying the results and ensuring that the maintenance work processes are followed.
- Risk &criticality
- Measuring the risk level ,as a result of the operation and maintenance work done to the asset , HSE performance, barrier reliability status or related indicators.
- Production assurance
- Defining and establishing of maintenance strategy and policy that commit the organization to a realizable level of performance. The goals focus on ambition level for;
- Assuring plant’s production as a result of the activities implemented to achieve and maintain a performance that is at its optimum in terms of the overall economy and production availability.
- Cost:
- Estimating and calculating and controlling cost that is under the of the maintenance function such as preventive and corrective work, spares and consumables, lost/deferred production