Reliability Centered Maintenance Solution
Today first priority in oil, gas and petrochemical industry is prolonged operation periods of their equipment without shutdown. Other words, extended shutdown-to-shutdown intervals is and effective strategy in this situation. This places extreme demands on the reliability of the plant equipment. The traditional methods of reliability assurance, like Preventive Maintenance, Predictive Maintenance and Condition Based Maintenance become inadequate in the face of such demands. Implementation of Reliability Centered Maintenance adopt this standardized methodology due to the complexity refiners and process plants equipment and the large amount of analysis that needs to be done.
What is Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM)?
RCM is a method to identify and select failure management policies to efficiently and effectively achieve the required safety, availability and economy of operation.
What are the key benefits?
- Intervals between shutdown/turnarounds are Increased
- Hidden failures and process trips are Decrease
- Mitigation of failures are improved by process monitoring
- Fully documented, consistent and integrated maintenance and operating plan for the entire asset
- Platform for creating operator-round process monitoring procedures
- Identification of “other reliability issues” such as design changes, procedure changes, potential
- Hidden failures, significant drawing errors and single point failures
- Identification equipment that were deemed “non-critical”, eliminating many unnecessary maintenance tasks
- Improving the reliability of the tag / equipment / system / plant / facility
Why Choose AIMS?
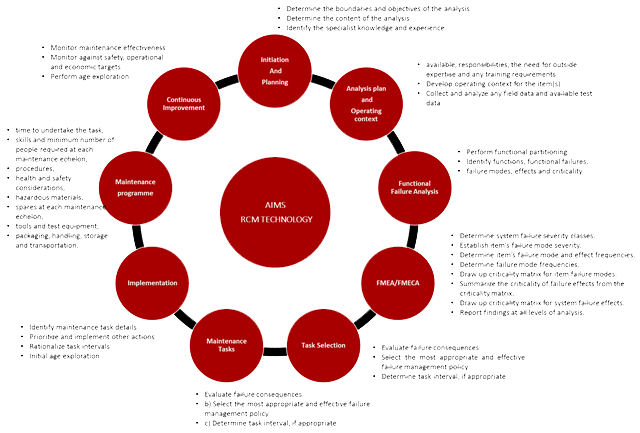
A core process in the development of a maintenance strategy and defining failure management policies AIMS , Reliability-Centered Maintenance service, based on IEC 60300-3-9 , is delivering a roadmap of appropriate tasks, frequencies, man-hours and skills mix and embedded with:
- Initiation and planning and Analysis plan and operating context
- Functional failure analysis and FMEA/FMECA
- Identifying failure causes and evaluate failure consequences
- Select the most appropriate and effective failure management policy
- determining applicable and cost-effective tasks to prevent the failures
- programming maintenance task detail
- Prioritize and implement other risk mitigation activities
- Monitor maintenance effectiveness, against safety, operational and economic targets
- Detraining continuous improvement